Digital Filters¶
Laboratory Class 08 - 14 October 2021
Implementation of a harmonic oscillator¶
Topics¶
Design of a first-order low-pass filter via bilinear transform:
from the Fourier transform of the real system’s response function to the z–transform of the simulator’s response function V (z);
difference equation and block diagram of the simulator;
implementation by using a pole placed at \(1-2^{-k}\);
dependency of the cutoff frequency \(f_{3dB} = 2\pi \omega_0 = (2\pi \tau)^{-1}\) on parameter k, provided that \(\omega_0T << 1\);
frequency behavior via “backward interpretation of the simulation theorem”.
Problems¶
implementation of a first-order low-pass filter;
assessment of the transfer function (to be displayed via Bode–diagrams).
Low pass filter¶
By applying the bilinear transform to the low-pass transfer function we get:
By inverting the z-transform we get:
Pole¶
If the pole is set to \(c=1-2^{-k}\) the cut of frequency becomes:
Summing up:
Implementation on FPGA¶
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
k = 10
tau = 1/(2*np.pi*50) # tau = 1/omega0 = 1/(2*pi*f3dB)
T = 2*np.pi*tau * 1/(100) # sampling time
c = 1-np.power(2, -k, dtype=float)
omega = np.logspace(start=-1, stop=6, num=1000, base=10)
V = (1-c)/2 * (2+1j*omega*T) / (1+1j*omega*T-c)
LP = 1/(1+1j*omega*tau)
y = np.abs(V)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(15, 7))
ax[0].plot(omega, y, label="Backward interpretation")
ax[0].plot(omega, np.abs(LP), label="True filder")
ax[0].axvline(x=2*np.pi*50, ymin=0, ymax=1, color="k", lw="0.5", label="50Hz")
ax[0].set_yscale('log')
ax[0].set_xscale('log')
ax[0].grid()
ax[0].legend()
ax[1].plot(omega, np.arctan(np.imag(V)/np.real(V))*180/(np.pi), label="Backward interpretation")
ax[1].plot(omega, np.arctan(np.imag(LP)/np.real(LP))*180/(np.pi), label="True filder")
ax[1].set_xscale('log')
ax[1].set_ylim([-90, 0])
ax[1].axvline(x=2*np.pi*50, ymin=0, ymax=1, color="k", lw="0.5", label="50Hz")
ax[1].legend()
ax[1].grid();
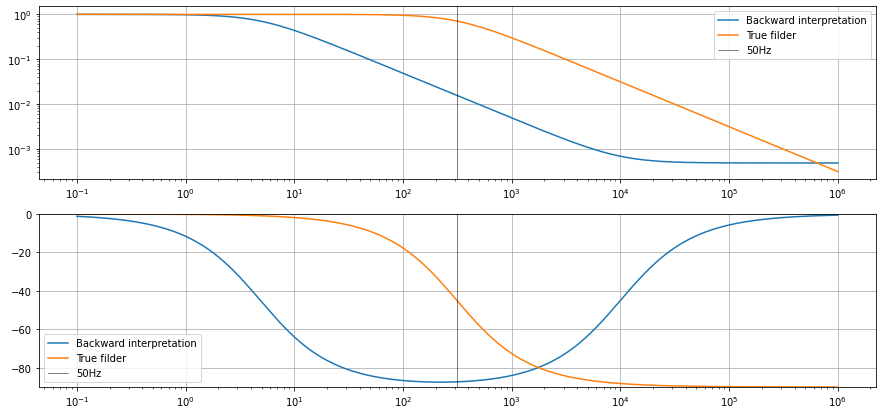
Remark: once we simulate the low pass filter a dependence on both the sampling time \(T_S\) and the parameter \(k = -log_{2}(1-c)\) is introduced. The sampling time is usually fixed so the only parameter left is \(k\).
Additional problems¶
Implementation of a sinusoidal oscillator by filtering – possibly with multiple LPFs in cascade – a square waveform.
Implementation of a notch filter.
Implementation of a phase-shifter (see Fig. 1 for the analog implementation to simulate).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kbcmLx5qDPk
https://circuitdigest.com/electronic-circuits/simple-square-wave-to-sine-wave-converter
